Back Pain
Overview
Back pain is a common condition characterised by discomfort or pain felt in the back, usually along the spine. It can vary in intensity, duration, and location, and may be acute or chronic. Back pain can affect people of all ages and can result from various causes. In some cases, pain can make it difficult or impossible to walk, sleep, work or do everyday activities. Many people with back pain will have associated radiating pain reaching the thigh, calf or foot called sciatica. Around four out of five people have back pain at some point in their lives.
Symptoms of back pain:
-
Stiffness
-
Muscle Spasms
-
Tenderness to Touch
-
Weakness or Numbness
-
Loss of Bowel or Bladder Control
-
It is severe and doesn’t improve with rest
-
Spreads down one or both legs, especially going below the knee (Sciatica)

Causes of Back Pain
Back pain refers to discomfort or distress experienced in the back region, encompassing the neck, upper back, and lower back. It ranges from a mild, temporary ache to severe, persistent pain and can result from muscle strains, ligament sprains, disc annular tears, herniated intervertebral discs, spinal vertebral compression fractures or other underlying medical conditions. Symptoms vary, including dull or sharp sensations, with potential radiation to the buttocks or legs. Back pain can be acute or chronic, impacting daily activities.
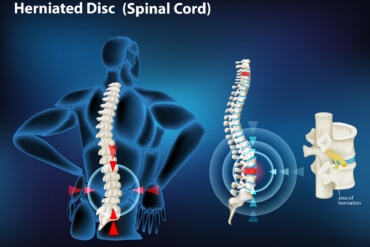
Bulging disks– Disks act as cushions between the bones in the spine. The soft material inside a disk can bulge or rupture and press on a nerve. Disk disease is often found on spine X-rays, CT scans or MRIs.
Facet Joint Pain: Facet joints are small joints located between each vertebra in the spine. Facet joint pain, or facet syndrome, occurs when these joints become inflamed or irritated.
Spinal Canal Stenosis: Spinal canal stenosis is a condition characterised by the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can lead to compression of the spinal cord and nerves. This narrowing may result from degenerative changes, herniated discs, bone spurs, or other factors.
Muscle or ligament strain- Repeated heavy lifting or a sudden awkward movement can strain back muscles and spinal ligaments. Constant strain on the back can cause painful muscle spasms.
Ankylosing spondylitis: Inflammatory arthritis affecting the spine, causing pain, stiffness, and fusion of vertebrae, often starting in young adulthood.
Back Pain Treatment Options
A physical exam by an IBAP doctor is often the first step to determining the source of pain. Following our doctor’s assessment, imaging tests, including X-rays, CT scans and MRIs, may be necessary to help doctors pinpoint the cause of the back pain and determine the best back pain treatment plan. Advanced, minimally invasive treatment options for back pain have improved outcomes and can help you return to the activities you enjoy. The treatment options from the Indo-British Advanced Pain Clinic that can help reduce back pain include
- Ozone Disc Nucleolysis
- Digital Spinal Analysis (DSA)
- Cooled radiofrequency ablation (C-RFA)
- Nerve Blocks
- Rest and physiotherapy, along with medication, can help reduce back pain.
- Kypho-Vertebroplasty
- Spinal cord Stimulation

Causes of back pain
Back pain often develops without a cause that shows up in a test or imaging study. Conditions commonly linked to back pain include:
1. Muscle or ligament strain- Repeated heavy lifting or a sudden awkward movement can strain back muscles and spinal ligaments. Constant strain on the back can cause painful muscle spasms.
2. Bulging disks- Disks act as cushions between the bones in the spine. The soft material inside a disk can bulge or rupture and press on a nerve. Disk disease is often found on spine X-rays, CT scans or MRIs.
3. Arthritis- Osteoarthritis can affect the lower back. In some cases, arthritis in the spine can lead to a narrowing of the space around the spinal cord, a condition called spinal stenosis.
4. Osteoporosis- The spine’s vertebrae can develop painful breaks if the bones become porous and brittle.
5. Ankylosing spondylitis- This inflammatory disease can cause some of the bones in the spine to fuse. This makes the spine less flexible.
Back Pain Treatment Options
A physical exam by an IBAP back pain doctor is often the first step to determining the source of pain. Following our back pain doctor’s assessment, imaging tests, including X-rays, CT scans and MRIs, may be necessary to help doctors pinpoint the cause of the back pain and determine the best back pain treatment plan.
Advanced, minimally invasive treatment options for back pain have improved outcomes and can help you return to the activities you enjoy. The treatment options from the Indo British advanced Pain clinic that can help reduce back pain include:
- Steroid Injections
- Nerve Blocks
- Rest and physiotherapy, along with medication, can help reduce back pain.
Some quick information
A common cause of back pain is mechanical injury or issue, such as a muscle sprains or joint irritation. However, in many cases, there is no clear cause.
There are many things that people can do to lower their risk of developing low back pain, including using proper lifting techniques, not smoking, and exercising regularly.
Low back pain is a common problem and can be caused by distinct factors, so Dr Vijay Bhaskar doesn’t believe there is a clear hereditary component to low back pain.
“We don’t typically recommend bed rest for lumbar spine problems anymore,” says Dr Vijay. Evidence has shown over time that bed rest actually makes the problem worse.
Our goal is to help the patient regain their quality of life
We relieve your pain, helping you be yourself again!

